ETC1010: Data Modelling and Computing
Lecture 4B: Advanced topics in data visualisation
Dr. Nicholas Tierney & Professor Di Cook
EBS, Monash U.
2019-08-23
While the song is playing...
Draw a mental model / concept map of last lectures content on joins.
recap
- Joins
- venn diagrams
- feedback
Upcoming Due Dates
- Assignment 2: Thursday 5th September, 5pm
- Stay tuned on ED for the upcoming dates
Making effective data plots
- Principles / science of data visualisation
- Features of graphics
Principles / science of data visualisation
- Palettes and colour blindness
- change blindness
- using proximity
- hierarchy of mappings
Features of graphics
- Layering statistical summaries
- Themes
- adding interactivity
Palettes and colour blindness
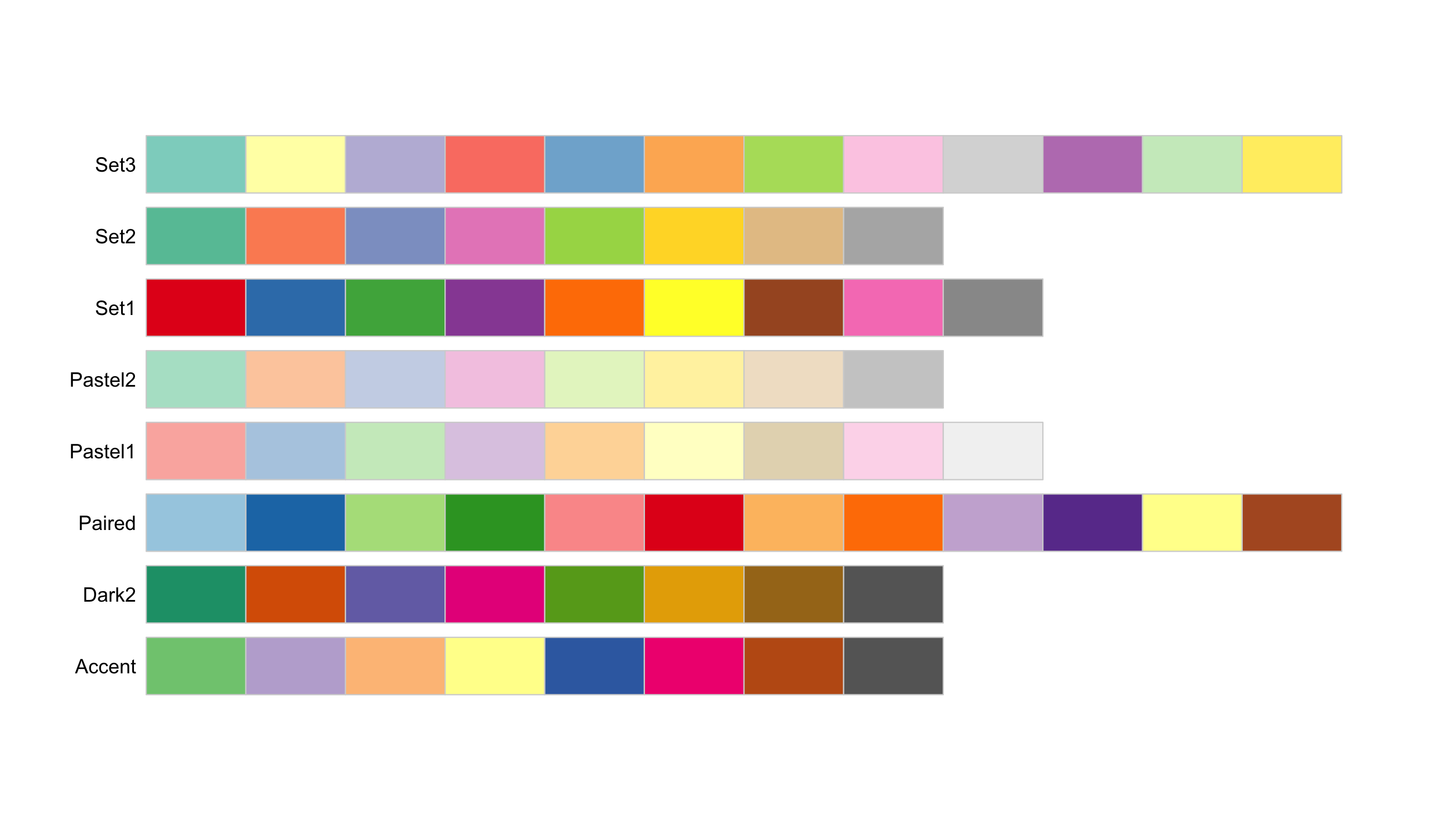
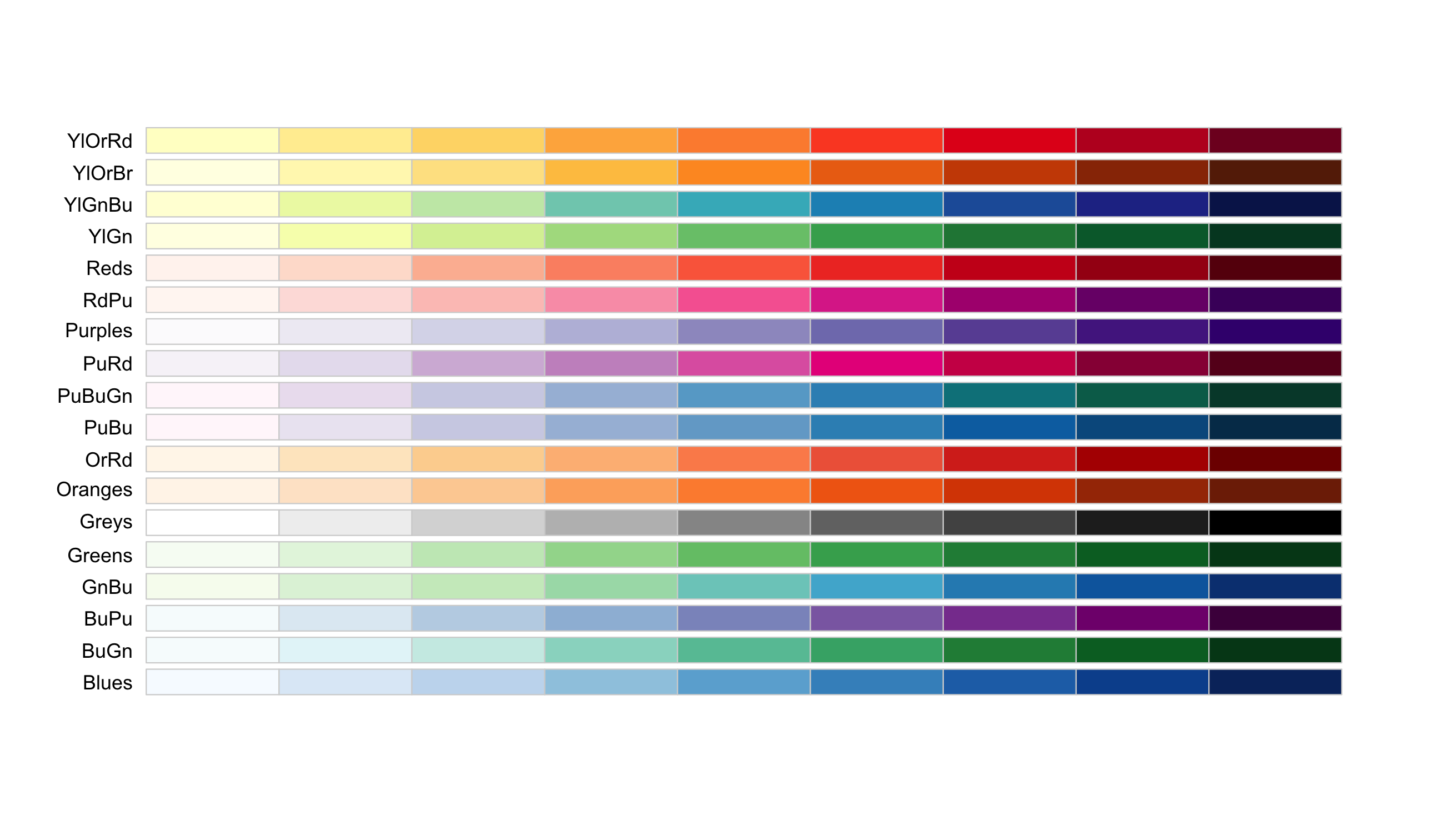
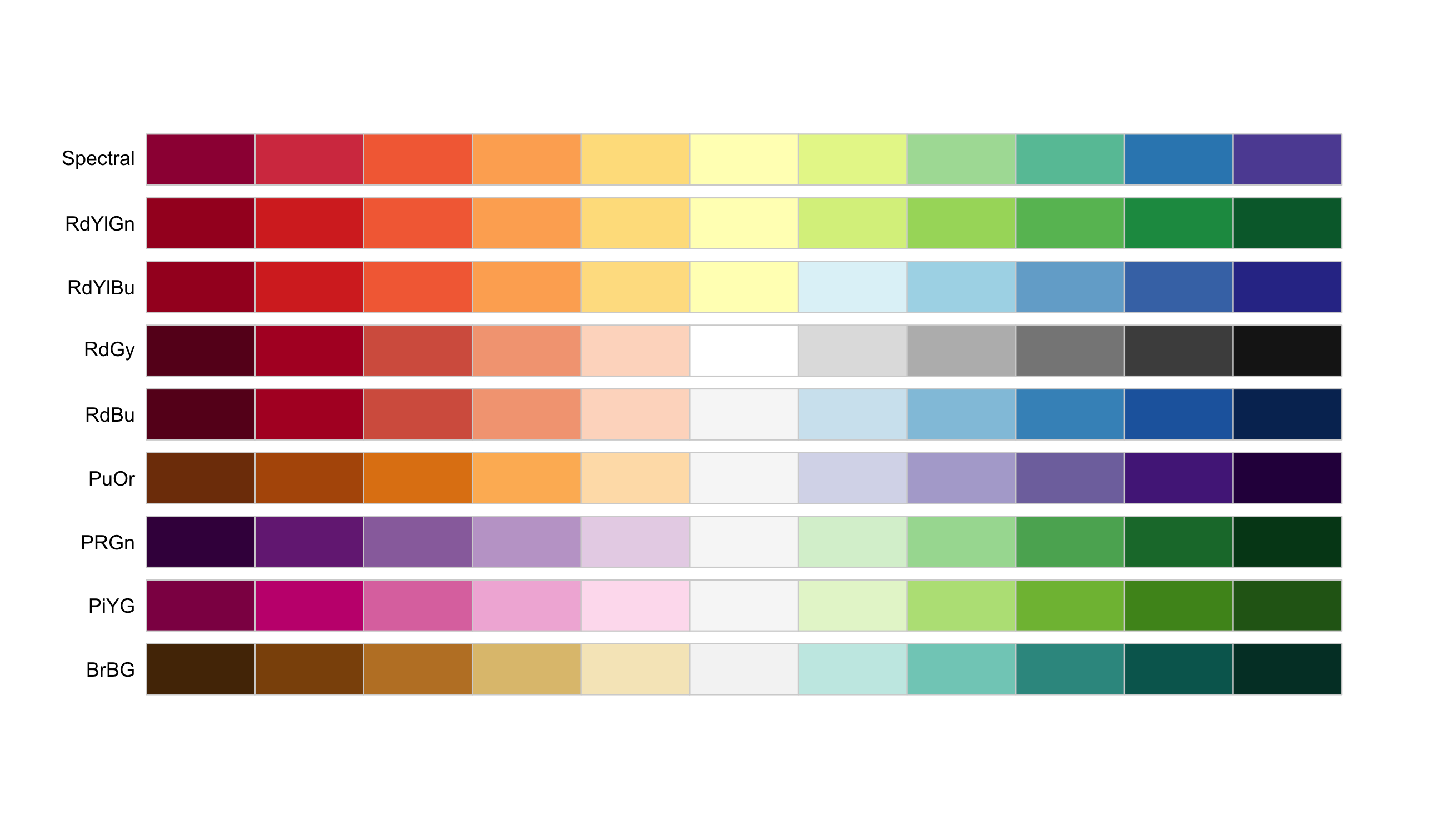
There are three main types of colour palette:
- Qualitative: categorical variables
- Sequential: low to high numeric values
- Diverging: negative to positive values
Qualitative: categorical variables

Sequential: low to high numeric values

Diverging: negative to positive values

Example: TB data
## # A tibble: 157,820 x 5## country year count gender age ## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <chr>## 1 Afghanistan 1980 NA m 04 ## 2 Afghanistan 1981 NA m 04 ## 3 Afghanistan 1982 NA m 04 ## 4 Afghanistan 1983 NA m 04 ## 5 Afghanistan 1984 NA m 04 ## 6 Afghanistan 1985 NA m 04 ## 7 Afghanistan 1986 NA m 04 ## 8 Afghanistan 1987 NA m 04 ## 9 Afghanistan 1988 NA m 04 ## 10 Afghanistan 1989 NA m 04 ## # … with 157,810 more rowsExample: TB data - adding relative change from 2002 - 2012
## # A tibble: 219 x 4## country `2002` `2012` reldif## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>## 1 Afghanistan 6509 13907 1.14 ## 2 Albania 225 185 -0.178 ## 3 Algeria 8246 7510 -0.0893## 4 American Samoa 1 0 -1 ## 5 Andorra 2 2 0 ## 6 Angola 17988 22106 0.229 ## 7 Anguilla 0 0 0 ## 8 Antigua and Barbuda 4 1 -0.75 ## 9 Argentina 5383 4787 -0.111 ## 10 Armenia 511 316 -0.382 ## # … with 209 more rowsExample: Sequential colour with default palette
ggplot(tb_map) + geom_polygon(aes(x = long, y = lat, group = group, fill = reldif)) + theme_map()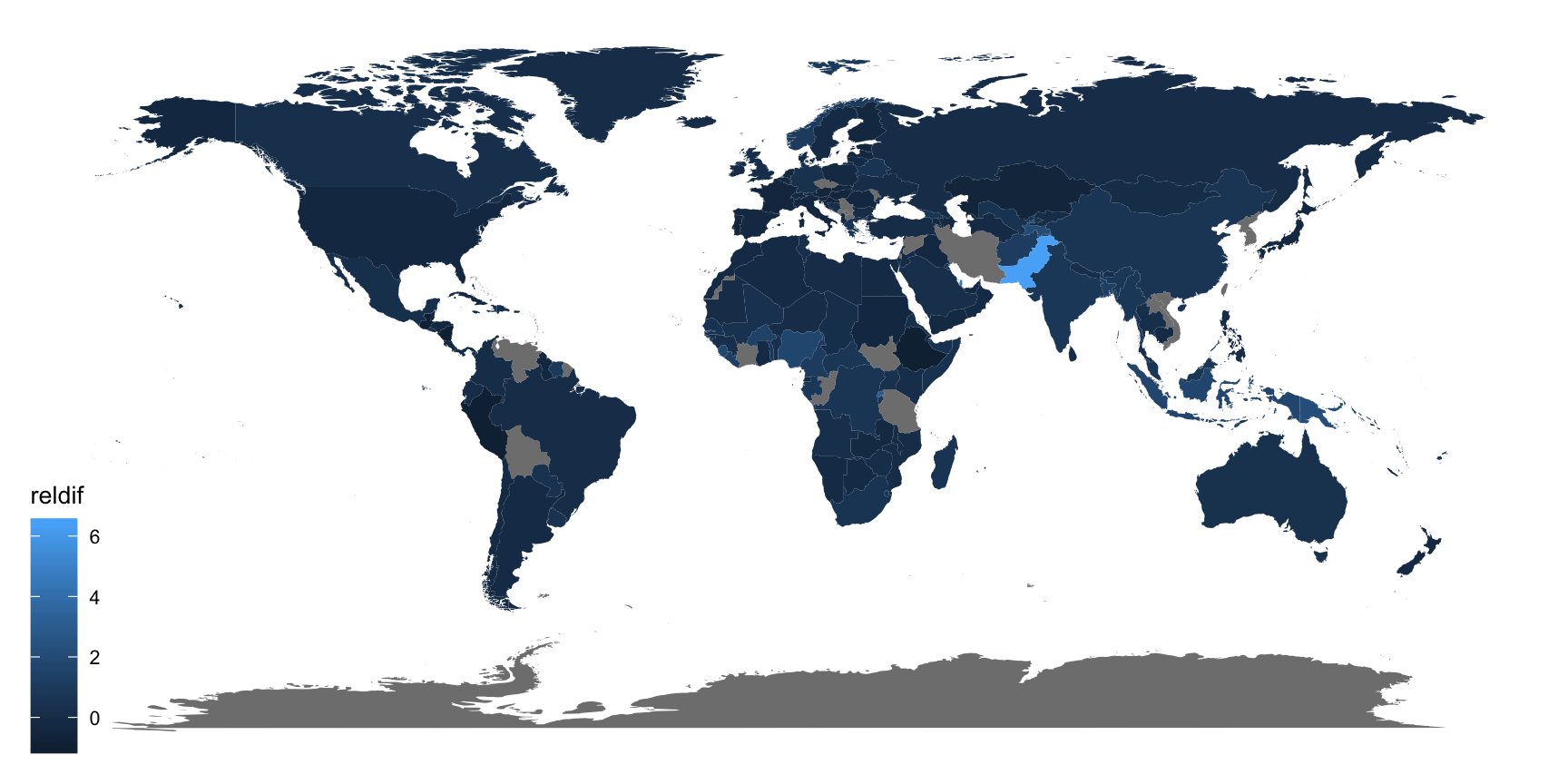
Example: (improved) sequential colour with default palette
library(viridis)ggplot(tb_map) + geom_polygon(aes(x = long, y = lat, group = group, fill = reldif)) + theme_map() + scale_fill_viridis(na.value = "white")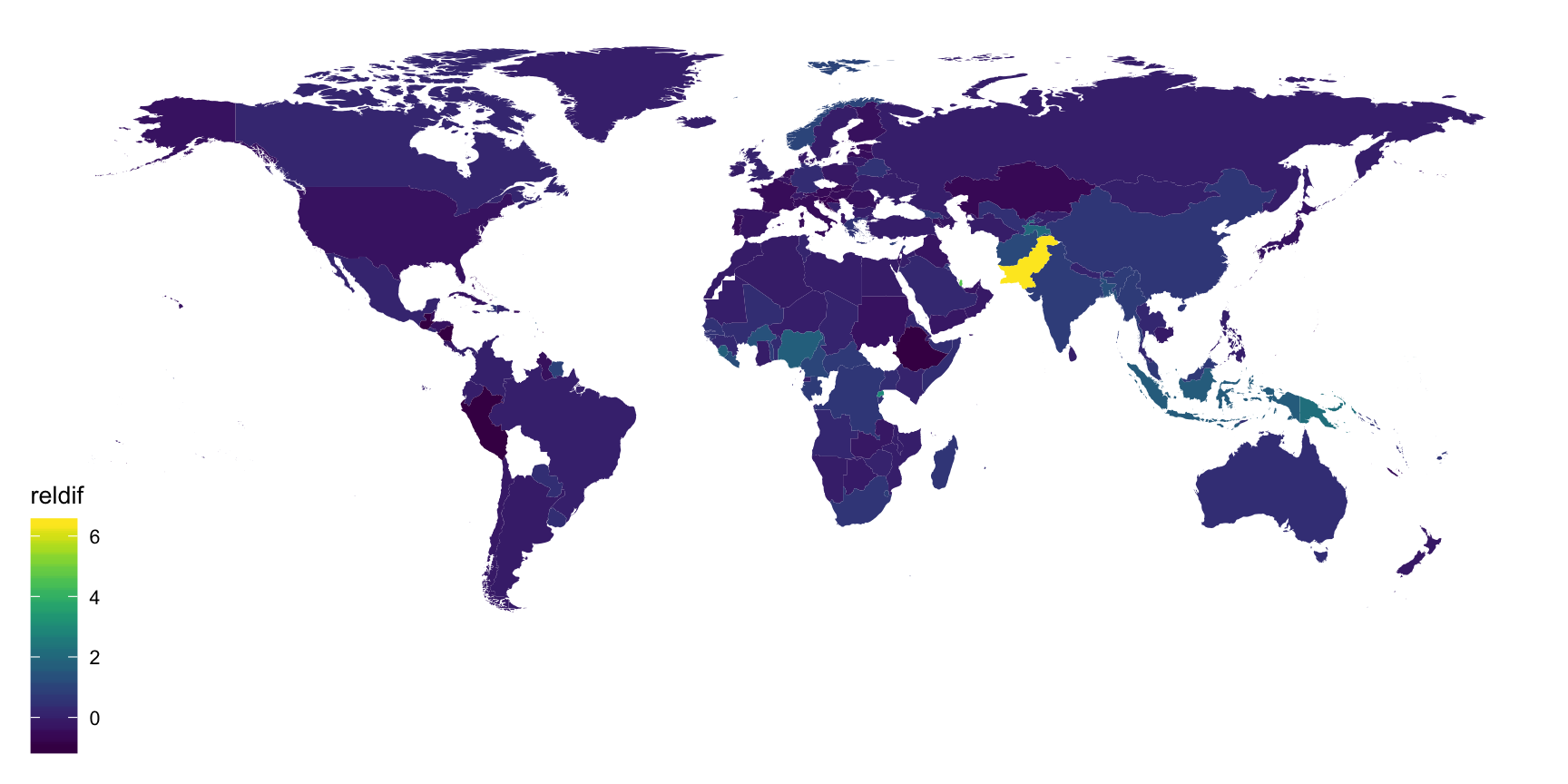
Example: Diverging colour with better palette
ggplot(tb_map) + geom_polygon(aes(x = long, y = lat, group = group, fill = reldif)) + theme_map() + scale_fill_distiller(palette = "PRGn", na.value = "white", limits = c(-7, 7))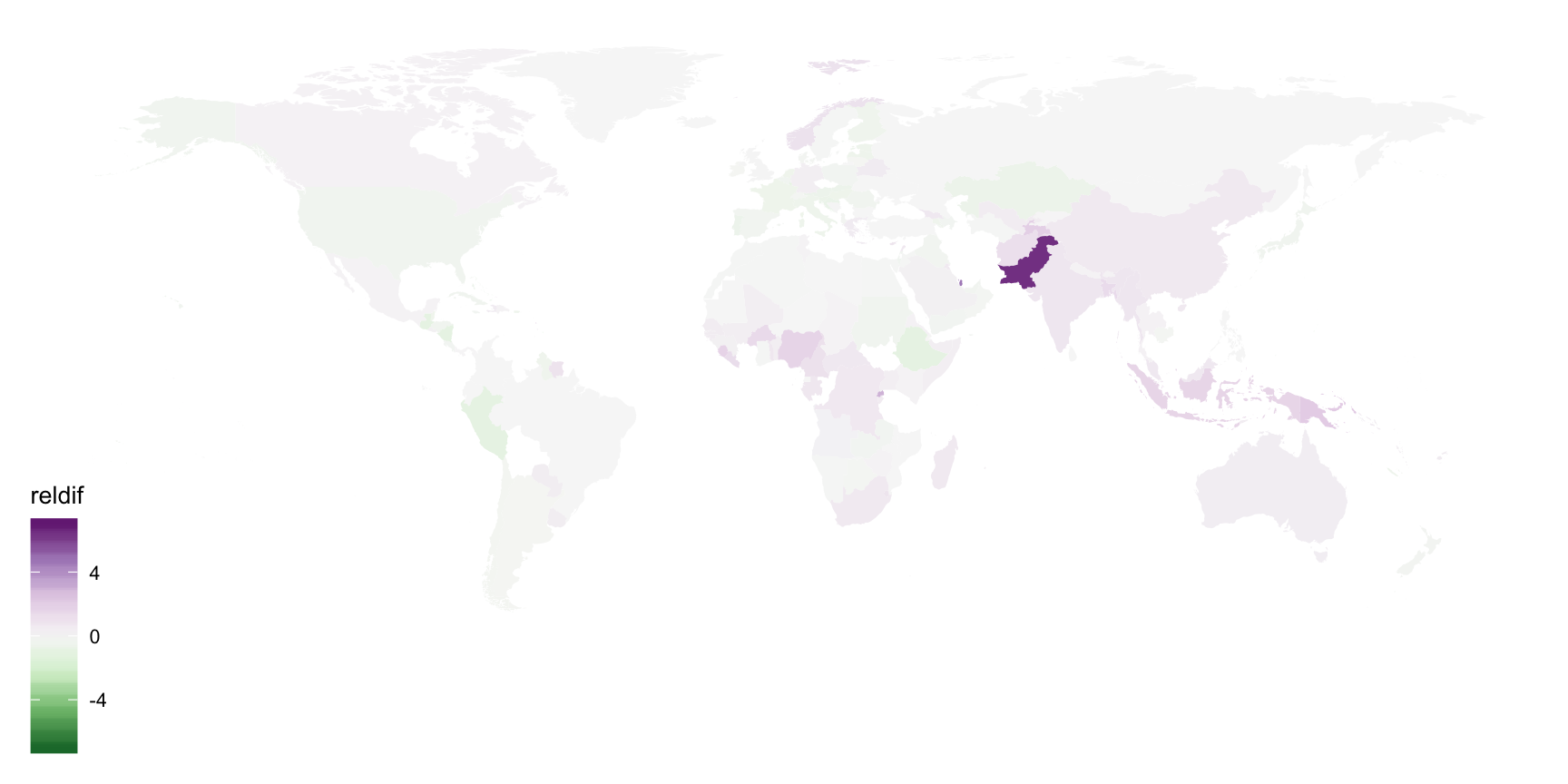
summary on colour palettes
- Different ways to map colour to values:
- Qualitative: categorical variables
- Sequential: low to high numeric values
- Diverging: negative to positive values
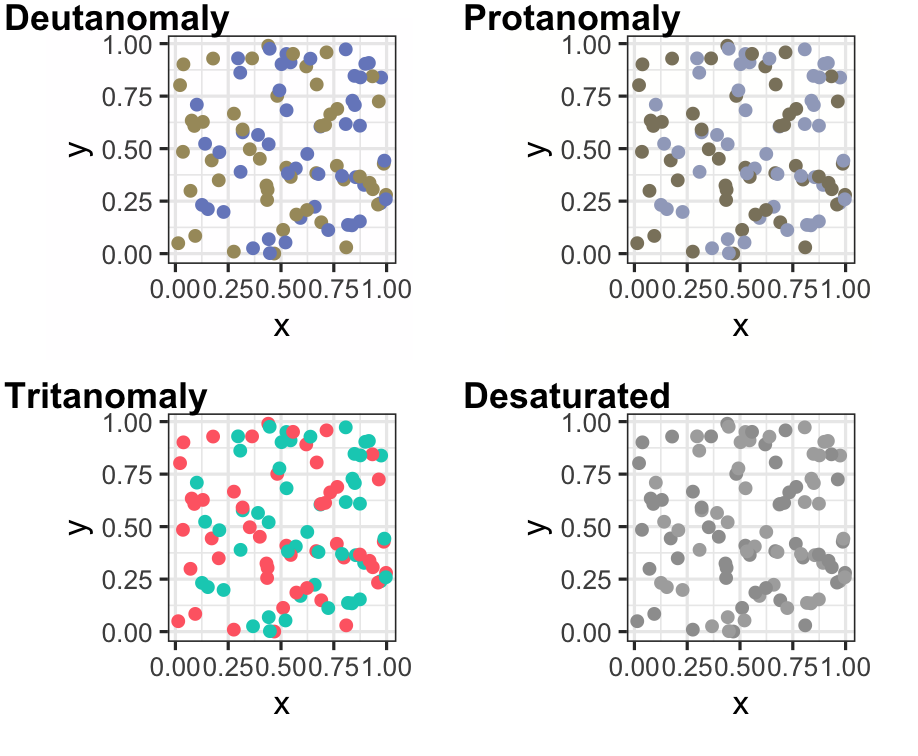
Colour blindness
- About 8% of men (about 1 in 12), and 0.5% women (about 1 in 200) population have difficulty distinguishing between red and green.
- Several colour blind tested palettes: RColorbrewer has an associated web site colorbrewer.org where the palettes are labelled. See also
viridis, andscico.
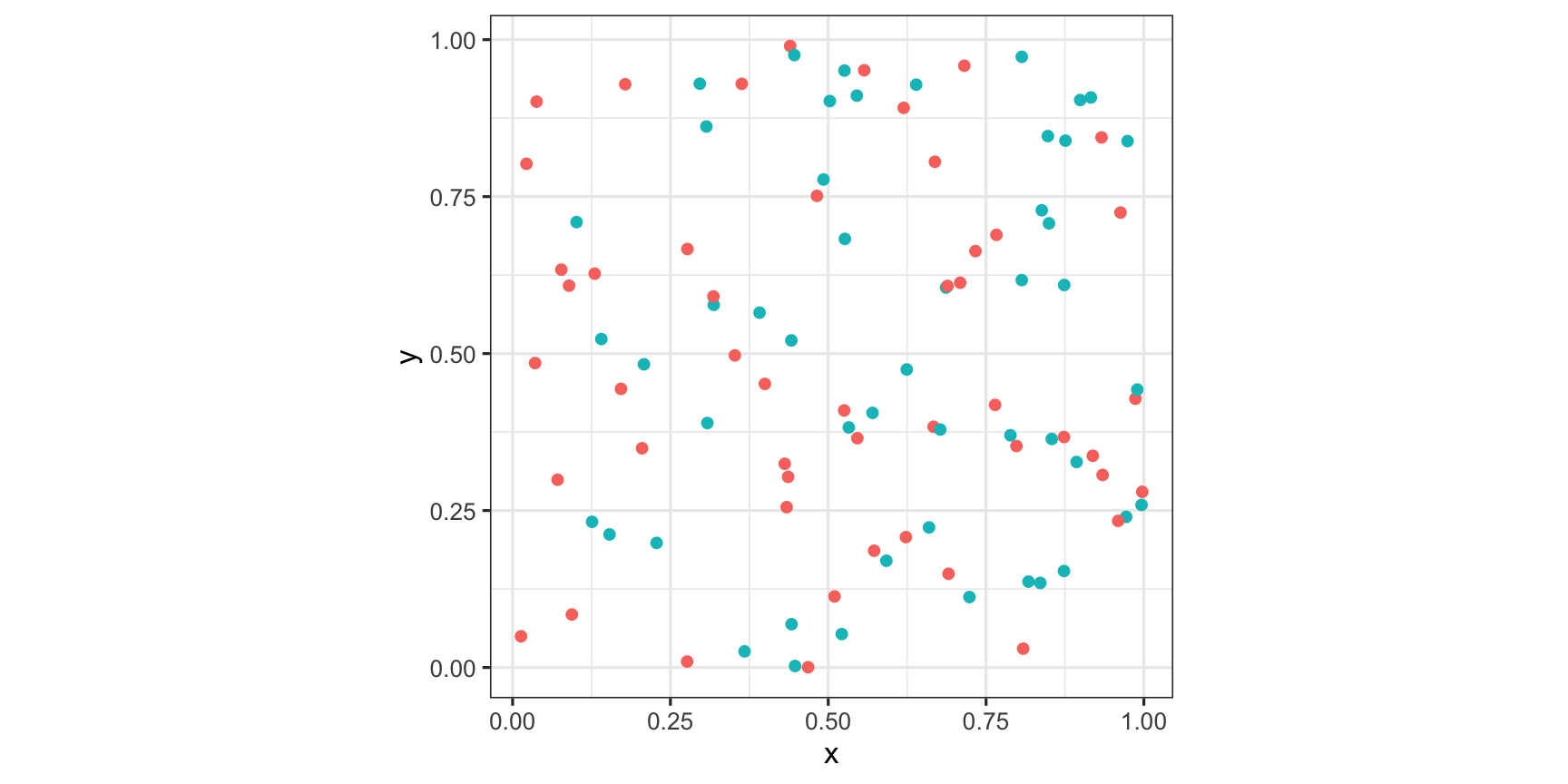
Plot of two coloured points: Normal Mode
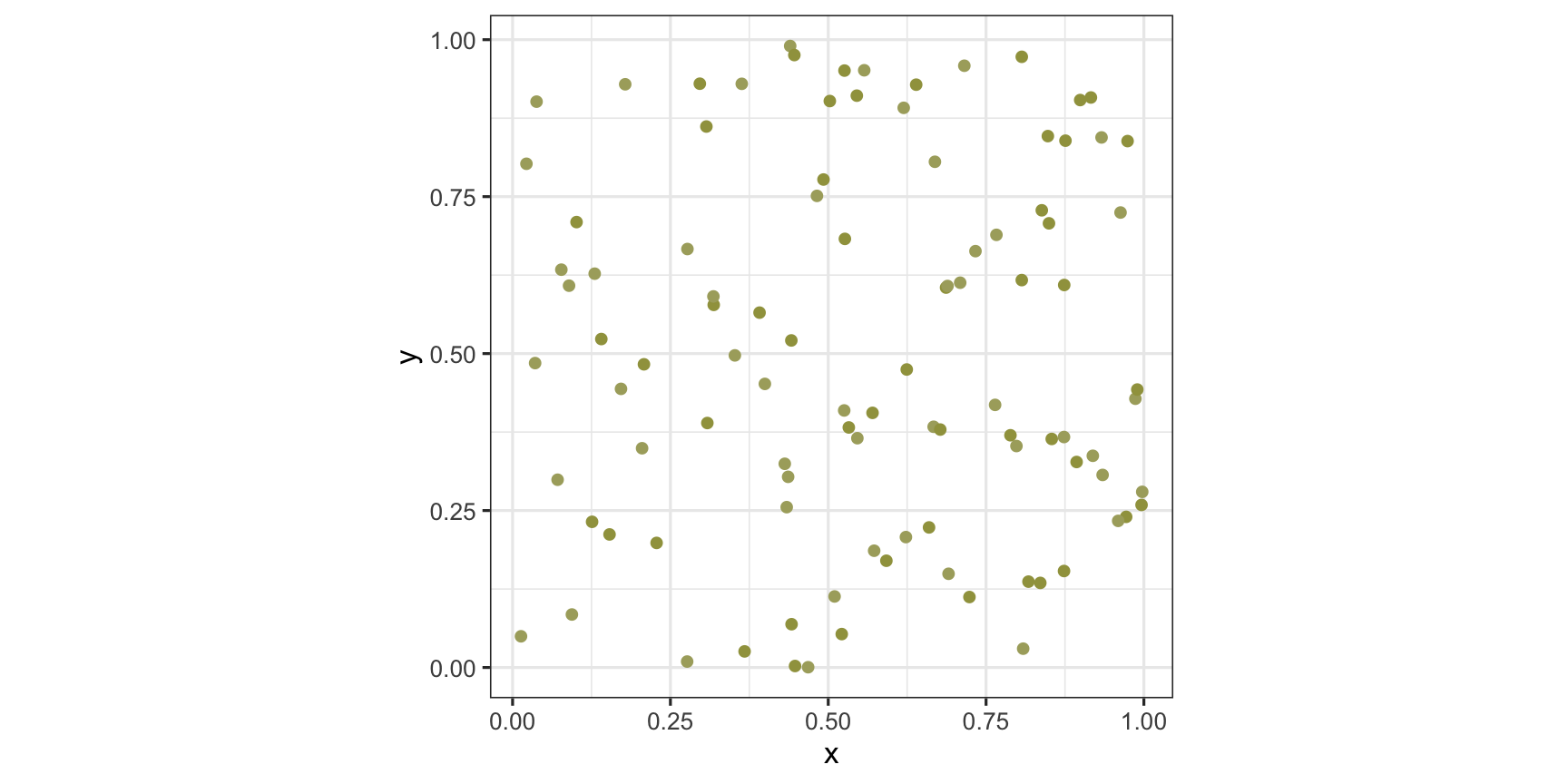
Plot of two coloured points: dicromat mode
p2 <- p + scale_colour_brewer(palette = "Dark2")p2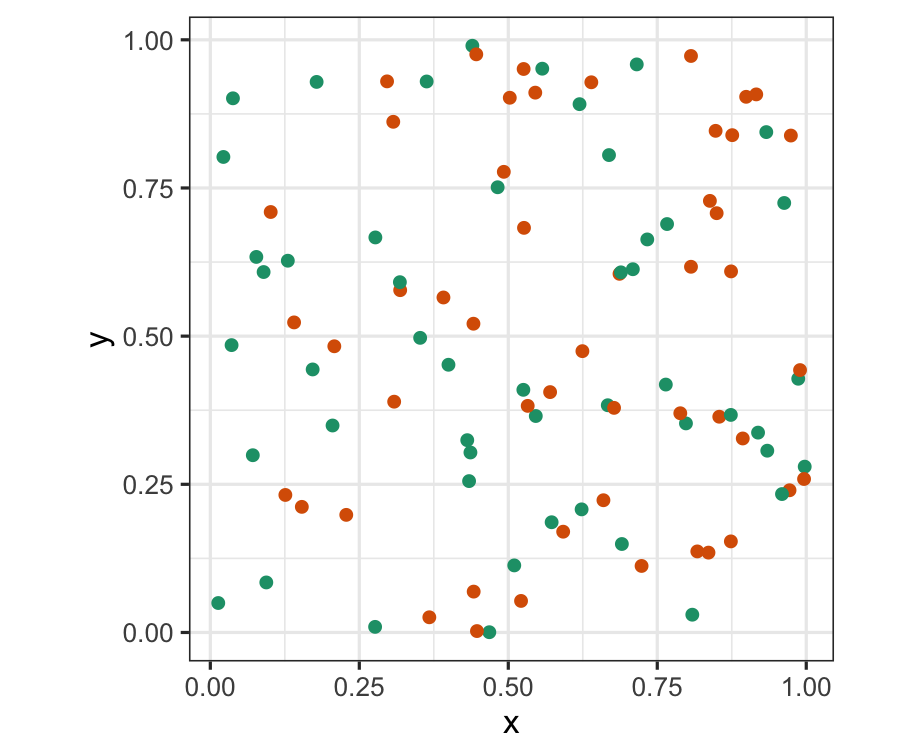
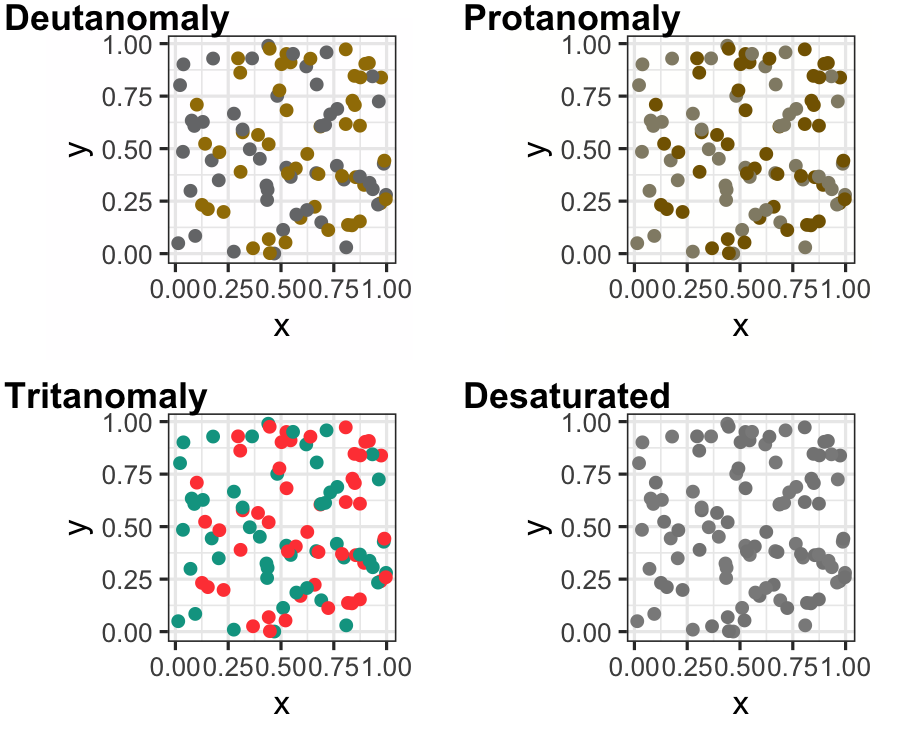
p3 <- p + scale_colour_viridis_d()p3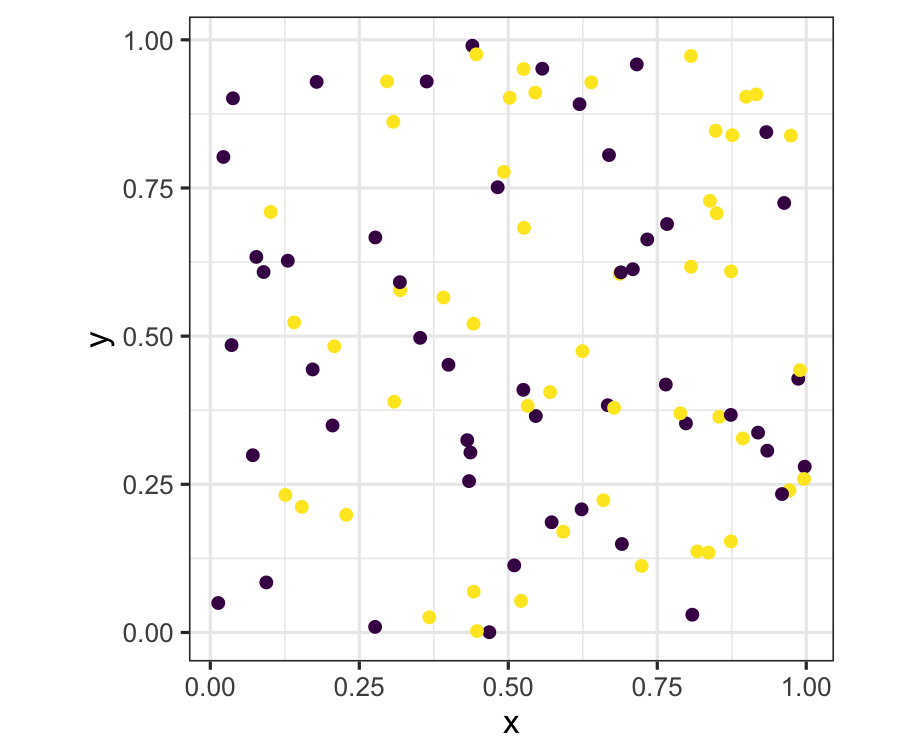
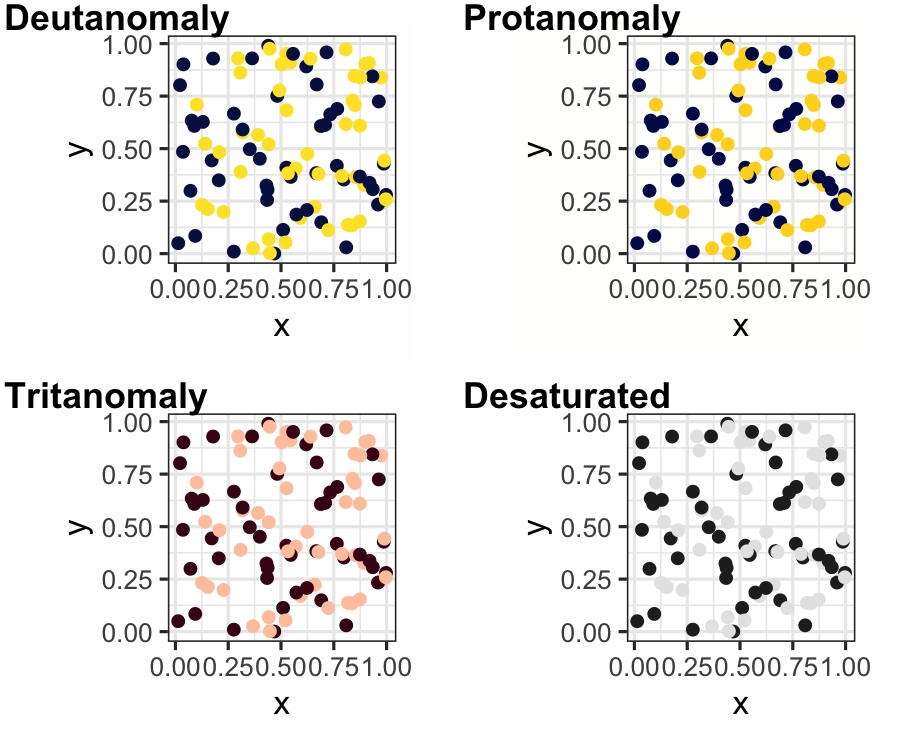
Summary colour blindness
- Apply colourblind-friendly colourscales
+ scale_colour_viridis()+ scale_colour_brewer(pallete = "Dark2")scicoR package
Pre-attentiveness: Find the odd one out?
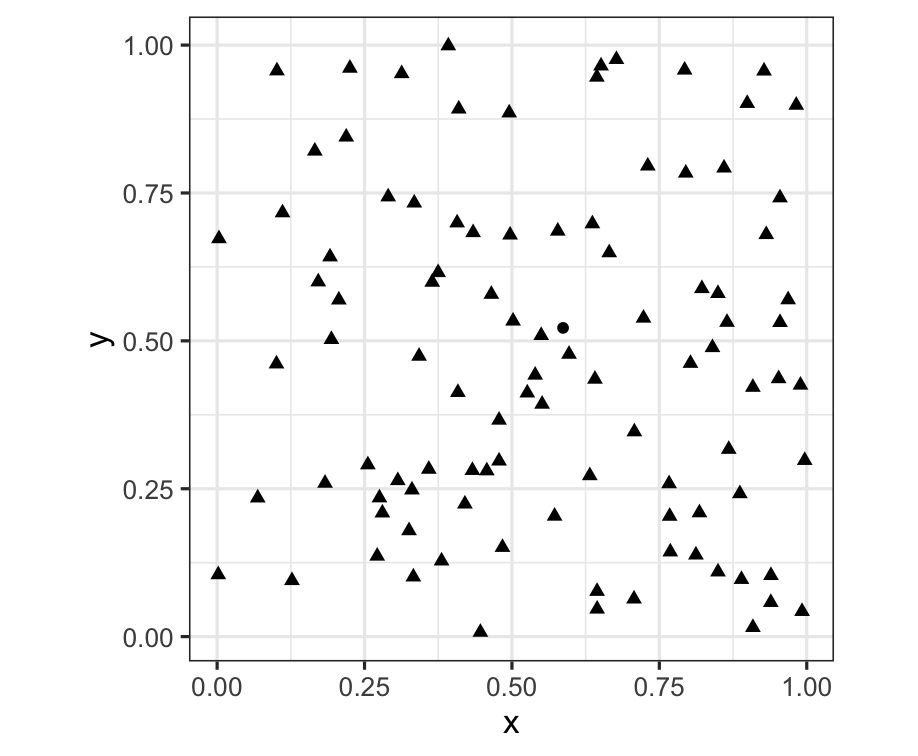
Pre-attentiveness: Find the odd one out?
Using proximity in your plots
Basic rule: place the groups that you want to compare close to each other
Which plot answers which question?
- "Is the incidence similar for males and females in 2012 across age groups?"
- "Is the incidence similar for age groups in 2012, across gender?"
...incidence similar for: (males and females) or (age groups, across gender) ?"
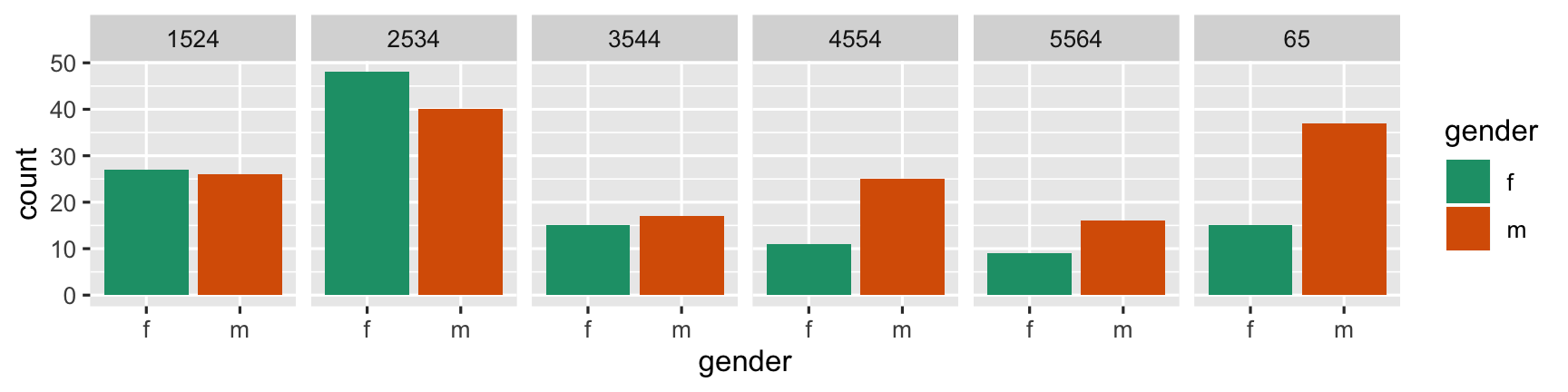
Here are two different arrangements of the tb data. To answer the question "Is the incidence similar for males and females in 2012 across age groups?" the first arrangement is better. It puts males and females right beside each other, so the relative heights of the bars can be seen quickly. The answer to the question would be "No, the numbers were similar in youth, but males are more affected with increasing age."
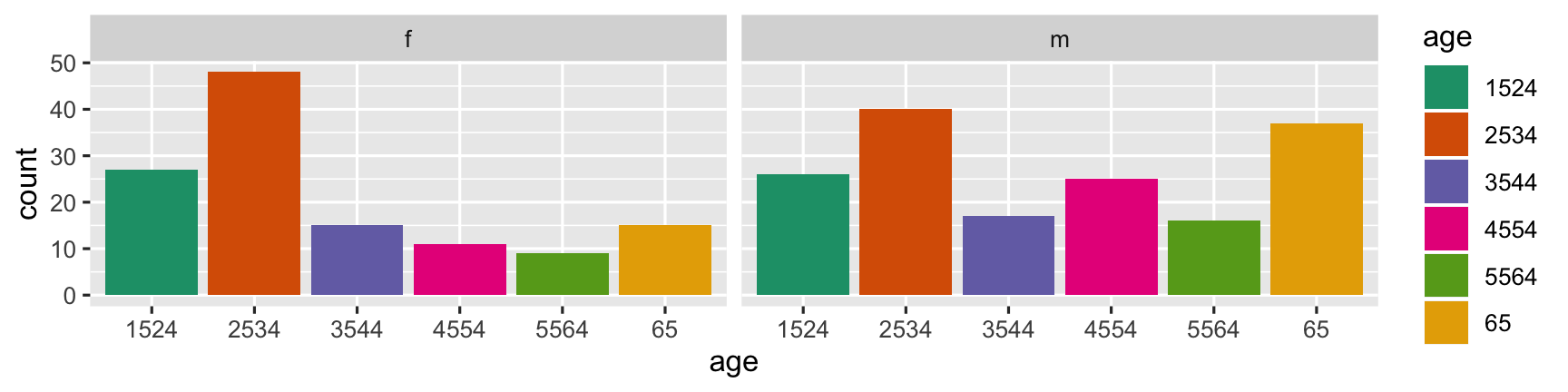
The second arrangement puts the focus on age groups, and is better to answer the question "Is the incidence similar for age groups in 2012, across gender?" To which the answer would be "No, among females, the incidence is higher at early ages. For males, the incidence is much more uniform across age groups."
"Is the incidence similar for males and females in 2012 across age groups?"
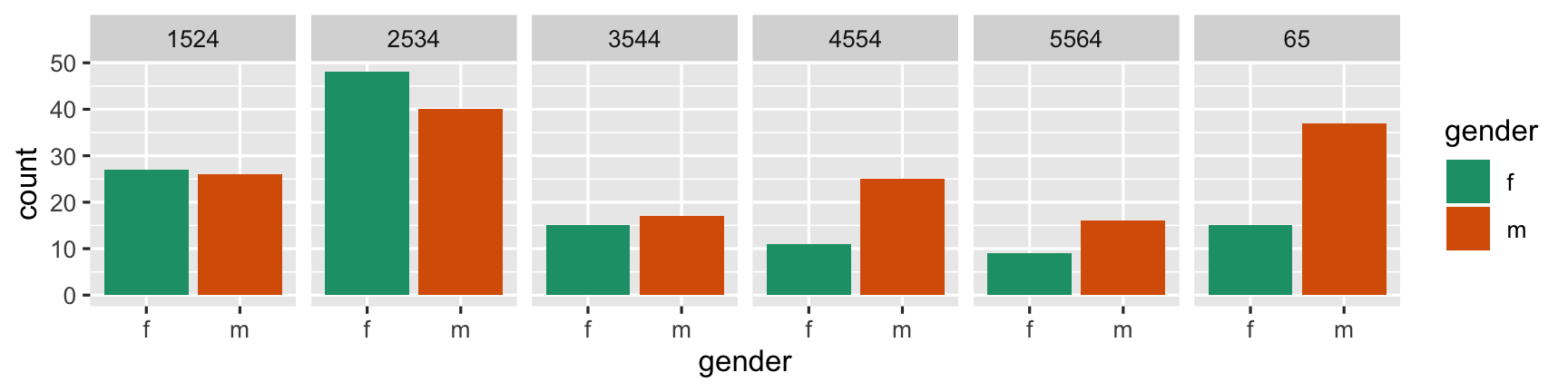
- Males & females next to each other: relative heights of bars is seen quickly.
- Auestion answer: "No, the numbers were similar in youth, but males are more affected with increasing age."
"Is the incidence similar for age groups in 2012, across gender?"
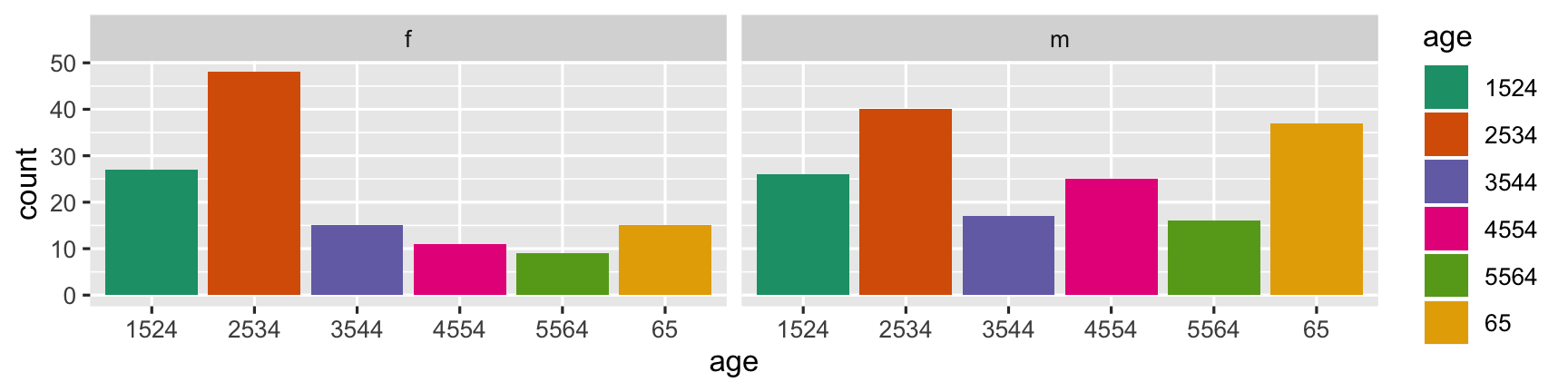
- Puts the focus on age groups
- Answer to the question: "No, among females, the incidence is higher at early ages. For males, the incidence is much more uniform across age groups."
Proximity wrap up
- Facetting of plots, and proximity are related to change blindness, an area of study in cognitive psychology.
- There are a series of fabulous videos illustrating the effects of making a visual break, on how the mind processes it by Daniel Simons lab.
- Here's one example:
The door study
Layering
- Statistical summaries: It is common to layer plots, particularly by adding statistical summaries, like a model fit, or means and standard deviations. The purpose is to show the trend in relation to the variation.
- Maps: Commonly maps provide the framework for data collected spatially. One layer for the map, and another for the data.
ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y1)) + geom_point()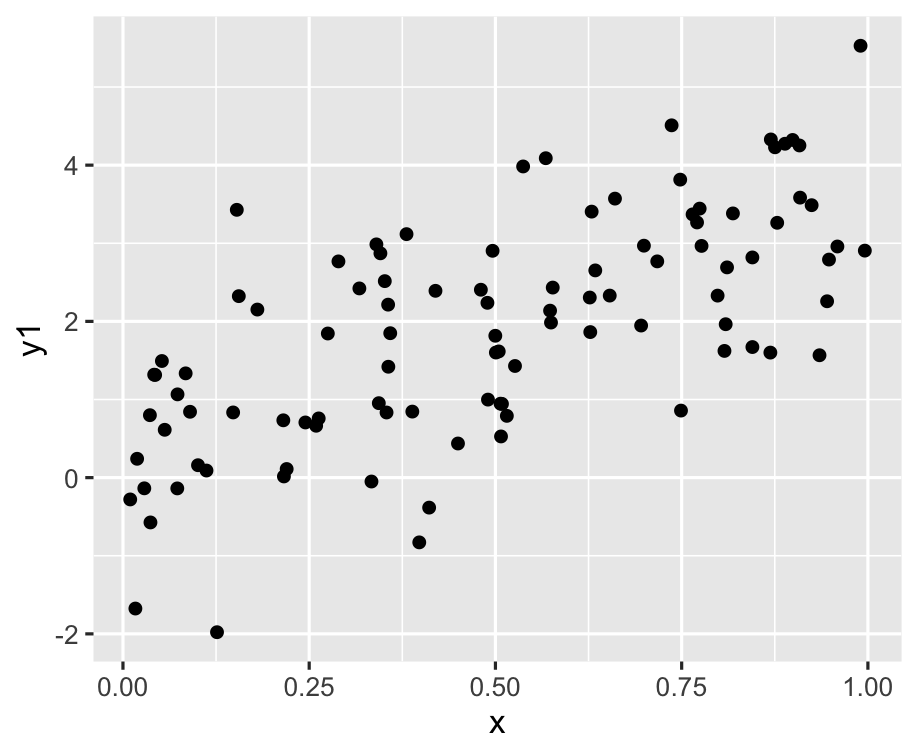
ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y1)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE)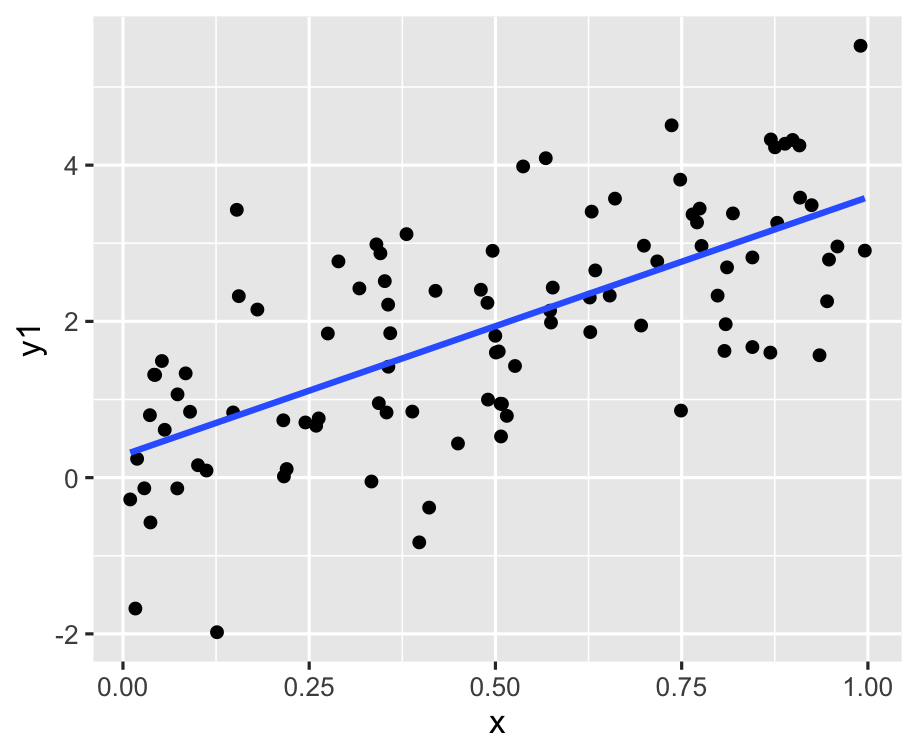
ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y1)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(method = "lm")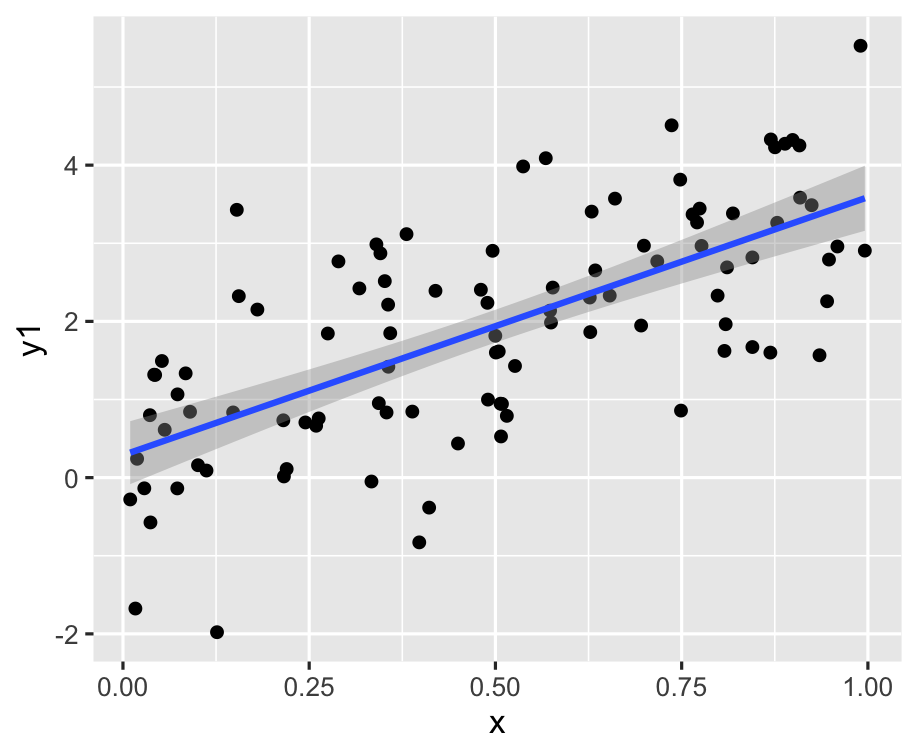
ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y2)) + geom_point()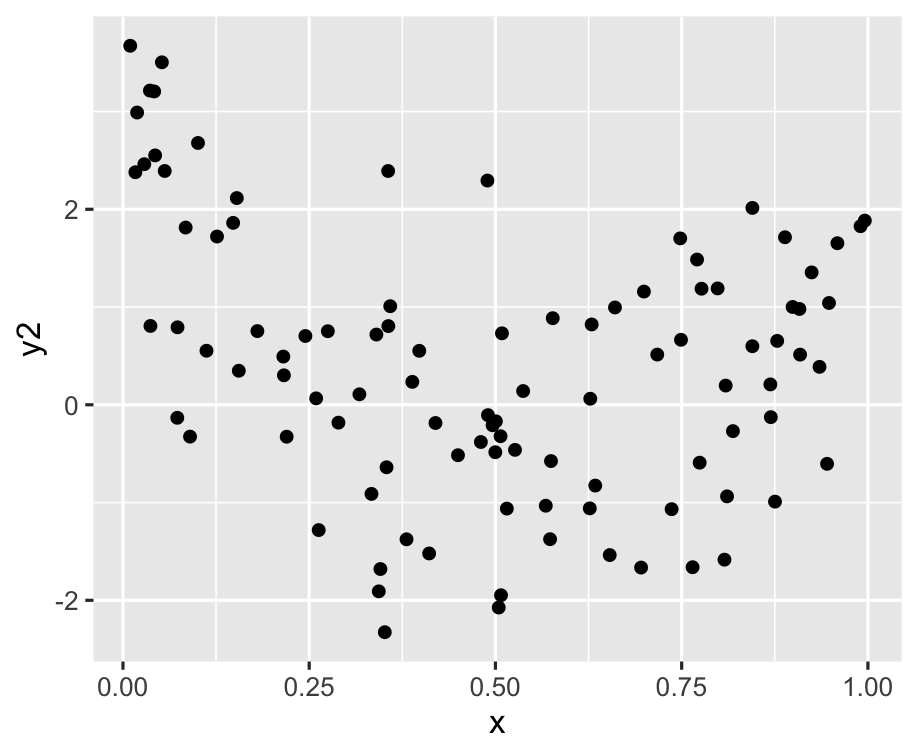
ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y2)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE)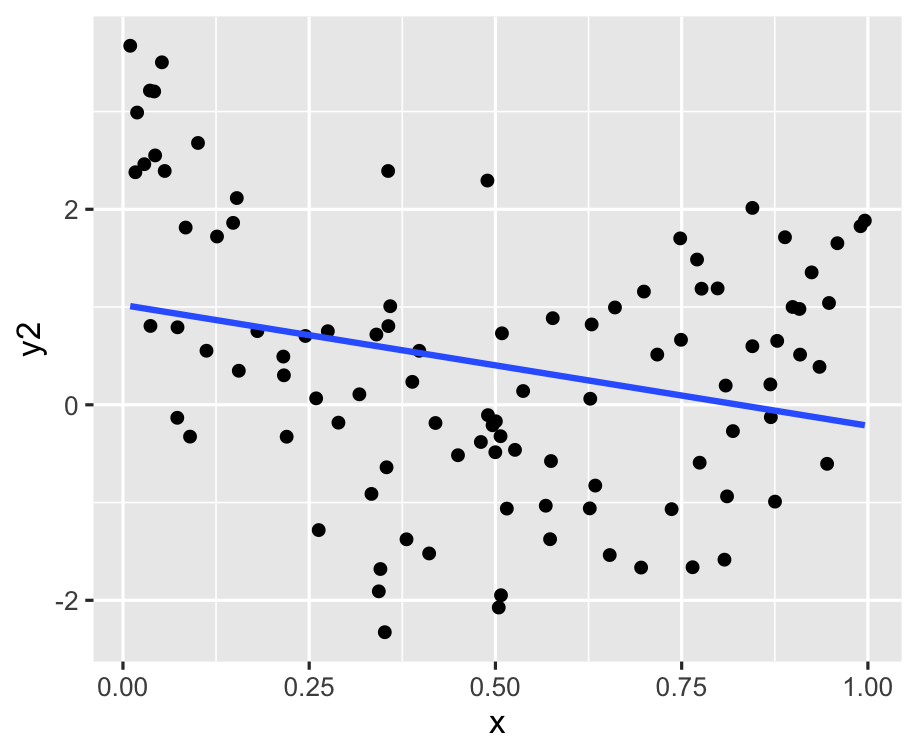
ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y2)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(se = FALSE)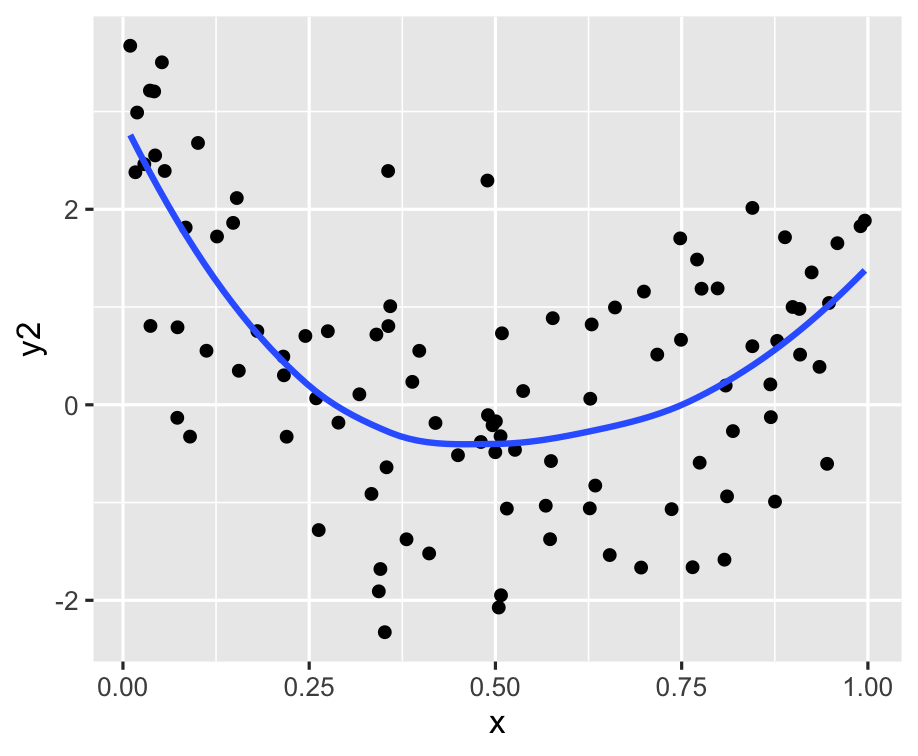
ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y2)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(se = FALSE, span = 0.05)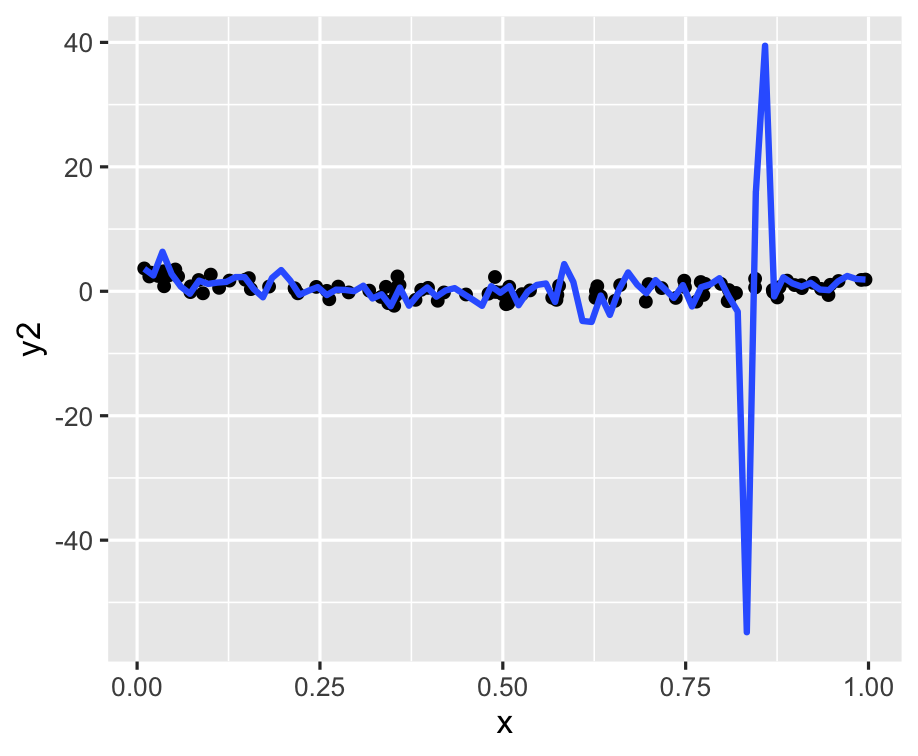
p1 <- ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y2)) + geom_point() + geom_smooth(se = FALSE, span = 0.2)p1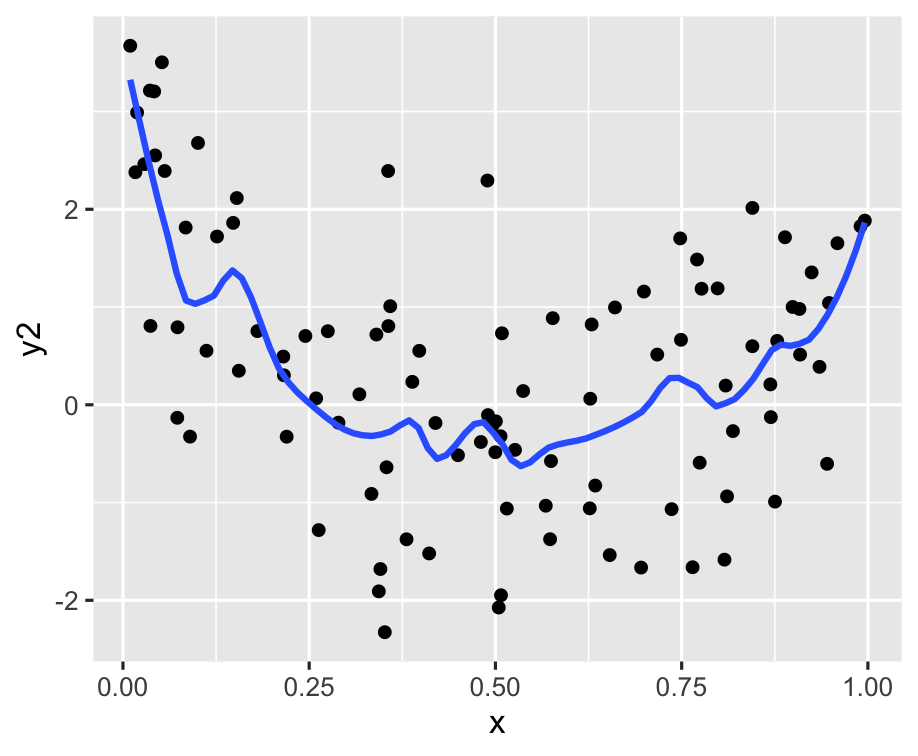
Themes: Add some style to your plot
p <- ggplot(mtcars) + geom_point(aes(x = wt, y = mpg, colour = factor(gear))) + facet_wrap(~am)p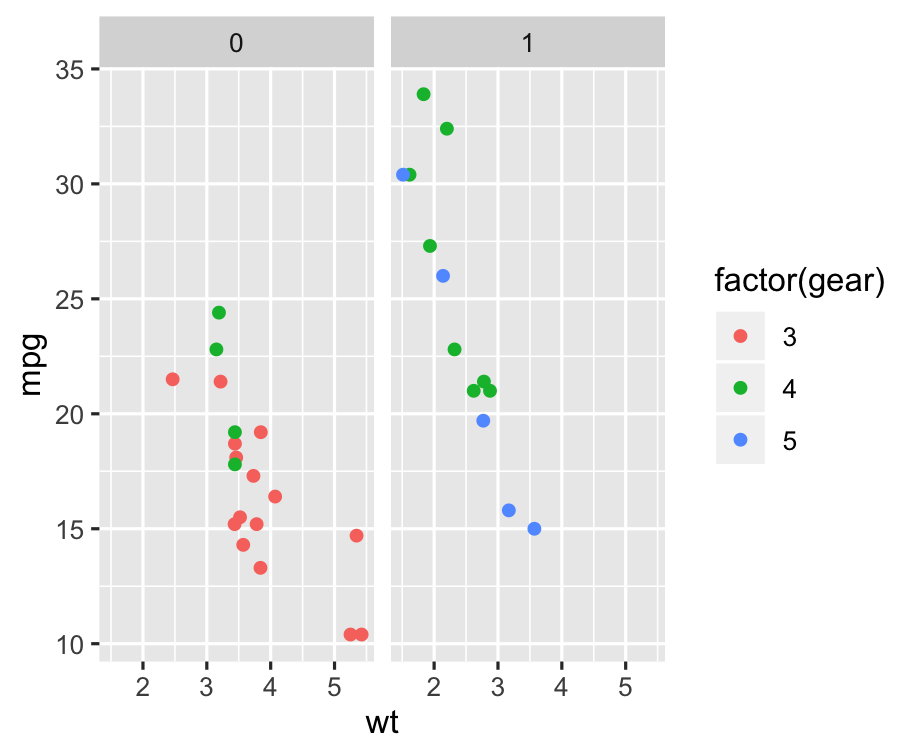
Theme: theme_minimal
p + theme_minimal()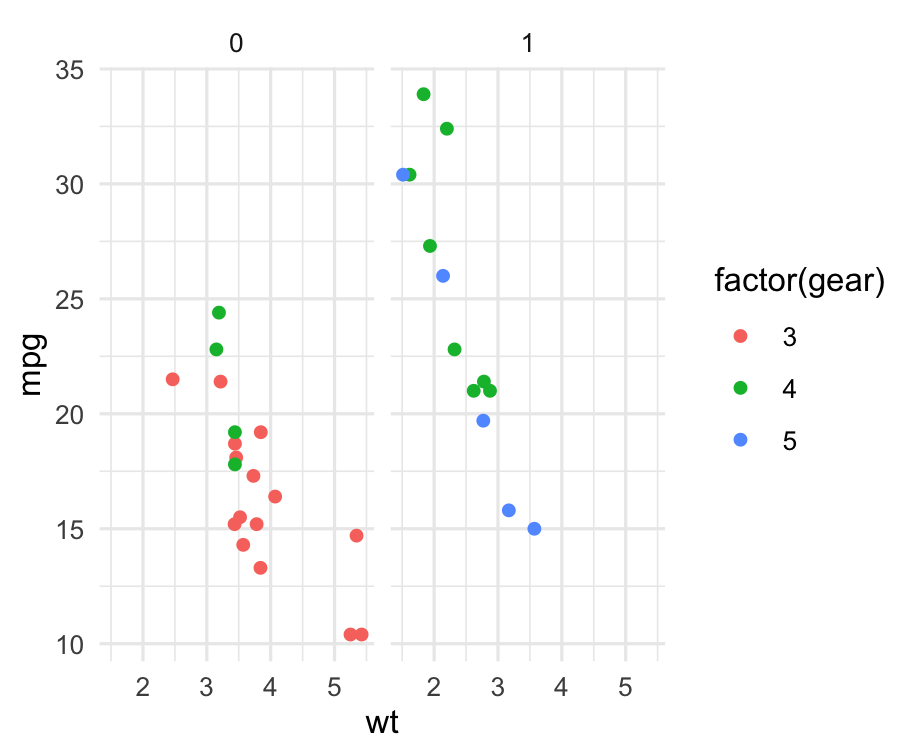
Theme: ggthemes theme_few()
p + theme_few() + scale_colour_few()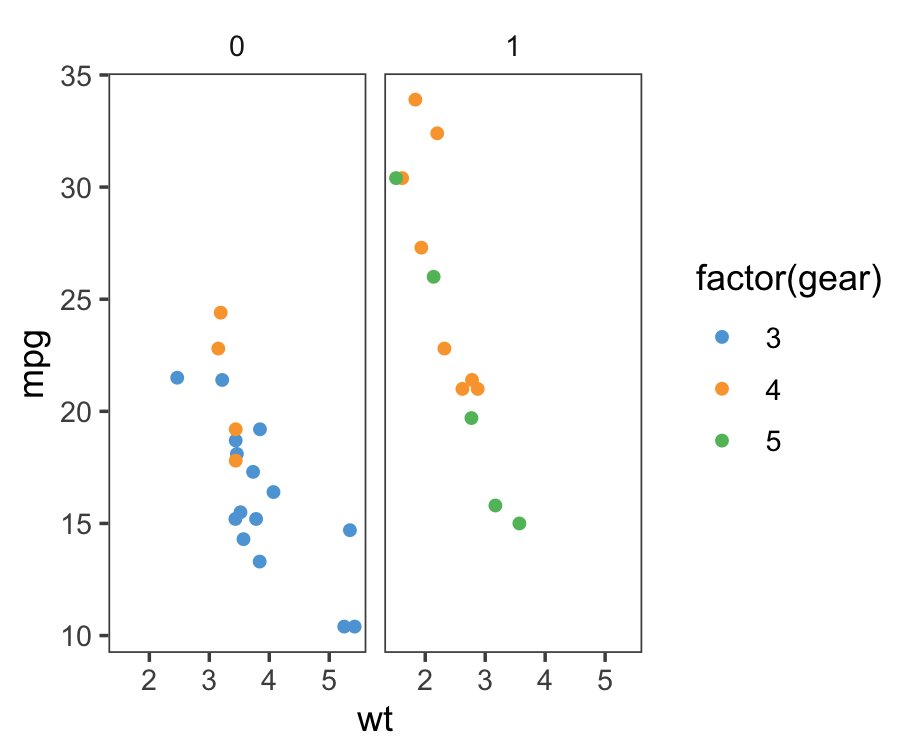
Theme: ggthemes theme_excel() 🤒
p + theme_excel() + scale_colour_excel()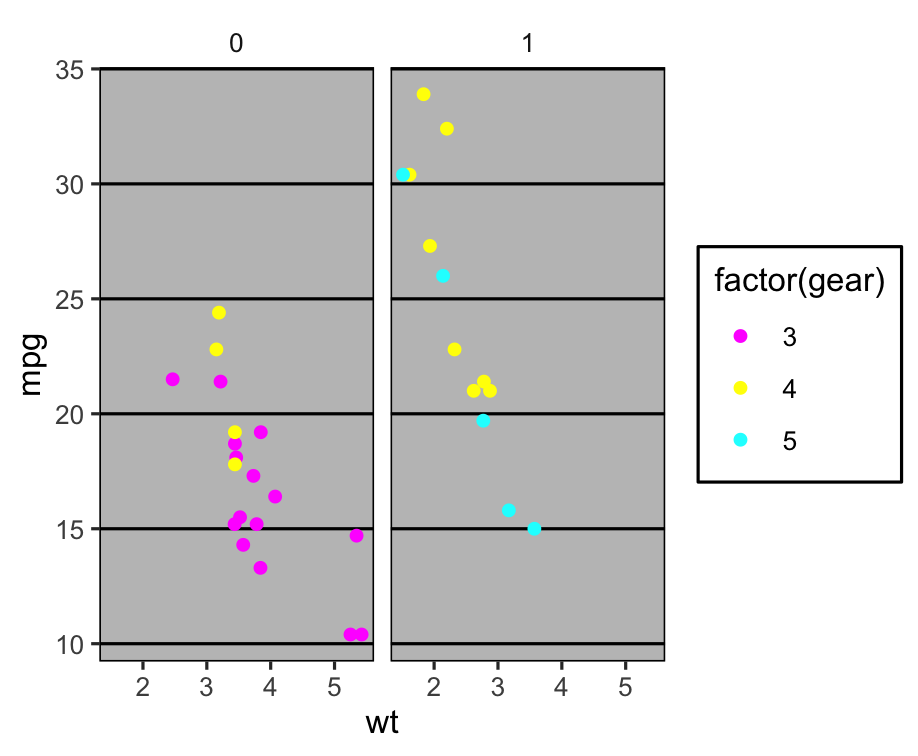
Theme: for fun
library(wesanderson)p + scale_colour_manual( values = wes_palette("Royal1") )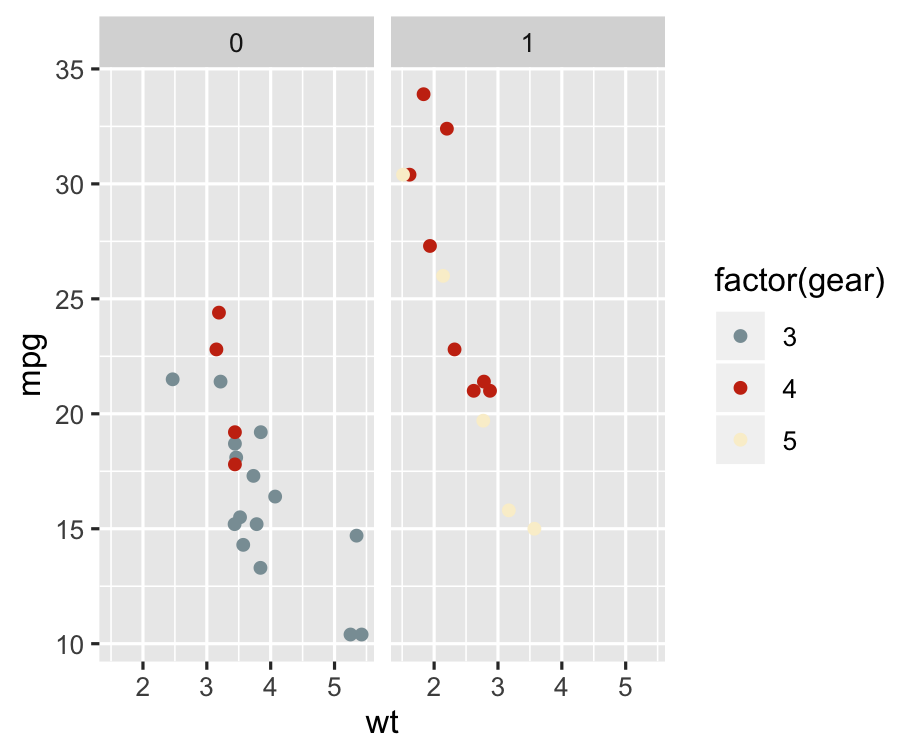
Summary: themes
- The
ggthemespackage has many different styles for the plots. - Other packages such as
xkcd,skittles,wesanderson,beyonce,ochre, ....
Hierarchy of mappings
- Position - common scale (BEST): axis system
- Position - nonaligned scale: boxes in a side-by-side boxplot
- Length, direction, angle: pie charts, regression lines, wind maps
- Area: bubble charts
- Volume, curvature: 3D plots
- Shading, color (WORST): maps, points coloured by numeric variable
Your Turn:
- lab quiz open (requires answering questions from Lab exercise)
- go to rstudio.cloud and check out exercise 4-B
- If you want to use R / Rstudio on your laptop:
- Install R + Rstudio (see )
- open R
- type the following:# install.packages("usethis")library(usethis)use_course("dmac.netlify.com/lectures/lecture4b/exercise/exercise-4b.zip")
Resources
- Kieran Healy Data Visualization
- Winston Chang (2012) Cookbook for R
- Antony Unwin (2014) Graphical Data Analysis
- Naomi Robbins (2013) Creating More Effective Charts
Share and share alike

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Variable types and mapping
| Type of variable | How to map | Common errors |
|---|---|---|
| Categorical, qualitative | Category + count/proportion displayed, often as an area plot or with a small number of categories mapped to colour or symbol | Not including 0 on the count/proportion axis. Not ordering categories. |
| Quantitative | Position along an axis | Displaying as a bar, especially when showing mean values. Mapping to colour. |
| Date/Time | Time-ordered axis, different temporal resolutions to study long term trend, or seasonal patterns. Lines typically connect measurements to indicate temporal dependence | Time order corrupted |
| Space | Conventional projections of the sphere, map aspect ratio | Wrong aspect ratio |
Coordinate systems
- Cartesian, polar: most plots are made in Cartesian coordinates. Just a few are in polar coordinates, primarily the pie chart. Polar coordinates use radius and angle to describe position in 2D space. Occasionally measurements like wind (direction and speed) make sense to be plotted in polar coordinates.
- fixed, equal: When variables are made on scales that should be comparable, it may be important to reflect this in the axes limits and page space that the plot takes. (This is different from
theme(aspect.ratio=1)which sets the physical size of the plot to be the same, or in some ratio.) - map: Maps come in conventional formats, most often with a specific aspect ratio of vertical to horizontal axes, that depends on latitude.
- flip: Useful for generating a plot with a categorical variable on the x axis and then flipping it sideways to look at.
df <- tibble(x = runif(100), y = runif(100) * 10)ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y)) + geom_point() + coord_fixed()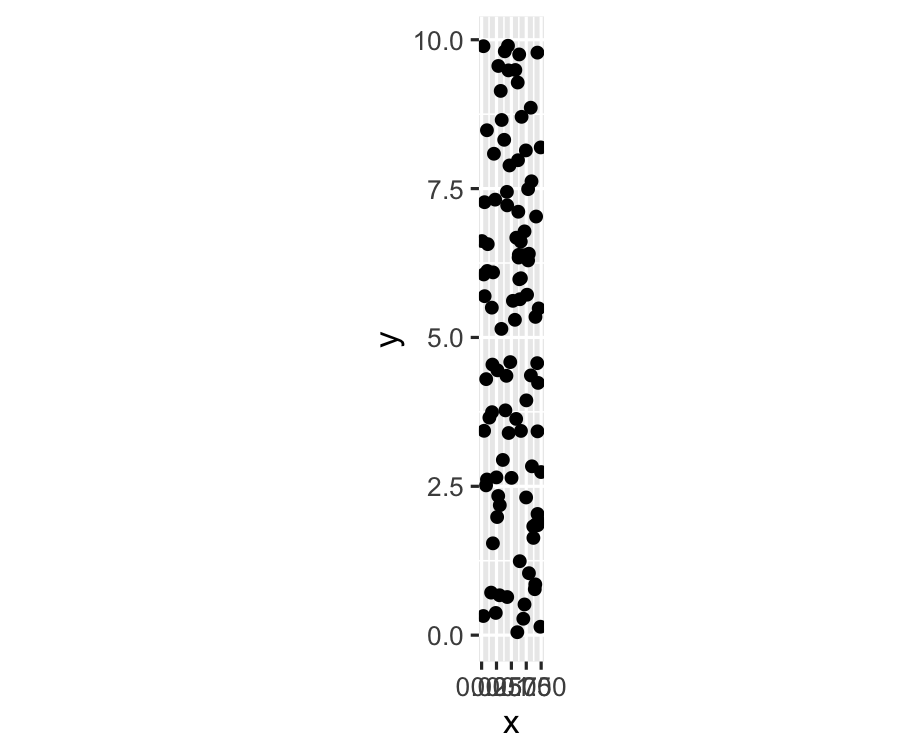
ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y)) + geom_point() + coord_equal()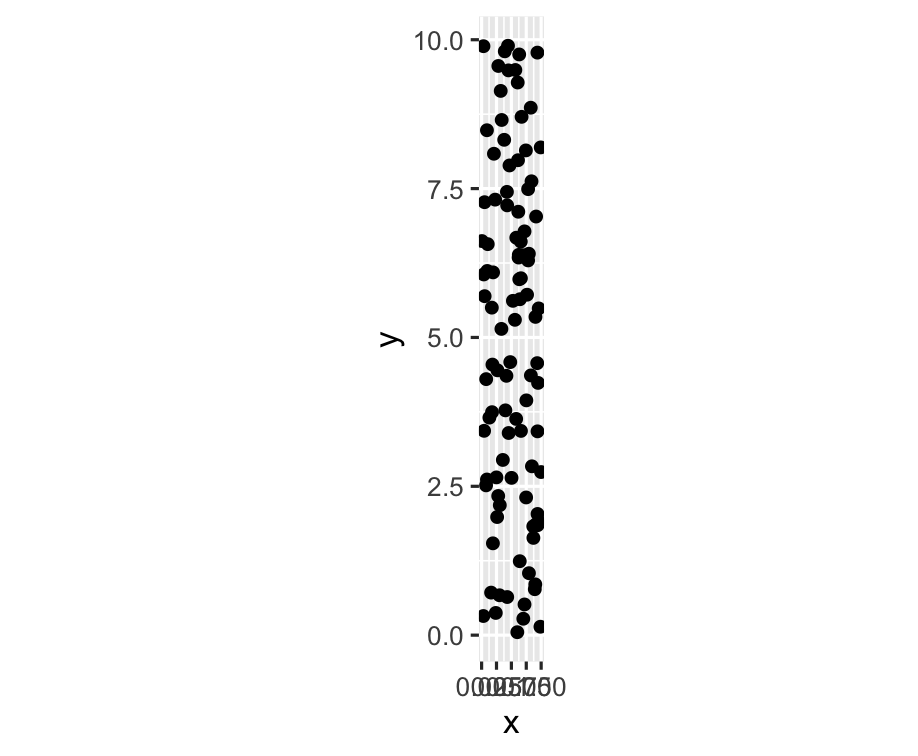
ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y)) + geom_point() + coord_fixed(ratio = 0.2)
ggplot(df, aes(x = x, y = y)) + geom_point() + theme(aspect.ratio = 1)
Adding interactivity to plots
Interaction on a plot can help de-clutter it, by making labels only show on mouse over. Occasionally it can be useful to zoom into parts of the plot. Often it is useful to change the aspect ratio.
The plotly package makes it easy to add interaction to ggplots.
library(plotly)p <- passengers %>% filter(type_of_flight == "INTL") %>% spread(key = bound, value = amount) %>% ggplot() + geom_point(aes(x = IN, y = OUT, label = airport)) + facet_wrap(~Year, ncol = 8) + coord_equal() + scale_x_continuous("Incoming passengers (mil)", breaks = seq(0, 8000000, 2000000), labels = seq(0, 8, 2)) + scale_y_continuous("Outgoing passengers (mil)", breaks = seq(0, 8000000, 2000000), labels = seq(0, 8, 2))ggplotly(p)